The right lateral paracolic gutter runs from the superiolateral aspect of the hepatic flexure of the colon down the lateral aspect of the ascending colon and around the cecum.
Paracolic gutter fluid ct.
Paracolic gutters function to drain fluid that leaks from the colon such as infectious matter pus or bile and to prevent infection or damage to the outer margin of the colon.
It is the depression between the postero lateral wall of the abdomen and the lateral margins of the ascending and descending colon.
This drainage occurs in much the same way that the gutters on a house draw the rain off the roof.
Fluid may sit within the peritoneal space or paracolic gutters or may be interposed between bowel loops or around solid organs e g.
Computed tomography ct is particularly.
Between the outer wall of the colon and back side of the abdominal wall there is an open space known as the paracolic gutter.
Etiologically it means a channel adjacent to the abdominal wall.
The ascending colon a is displaced anteriorly and ascites arrowhead is seen in the right paracolic gutter.
Fluid from the stomach duodenum or gallbladder may run down the gutter to collect in the right iliac fossa or pelvis and may mimic acute appendicitis or form a pelvic abscess.
The inframesocolic space also contains paracolic gutters which are peritoneal recesses that are inferolateral extensions of their corresponding inframesocolic spaces on the posterior abdominal wall lateral to the ascending and descending colon respectively.
It is also known as sulci paracolic and paracolic recesses.
It can be compared to fluid in the gallbladder or stomach.
Dense fluid may suggest hemoperitoneum especially in the context of trauma.
The main paracolic gutter lies lateral to the colon on each side.
General ct findings of early and late stage pid include thickening of the uterosacral ligaments pelvic fat stranding with obscuration of fascial planes reactive lymphadenopathy and pelvic free fluid.
A less obvious medial paracolic gutter may be formed especially on the right side if the colon possesses a short mesentery for part of its length.
Laparotomy was performed 6 hours after ct.
Given the nonspecific clinical manifestations computed tomography ct is commonly the first imaging examination performed.
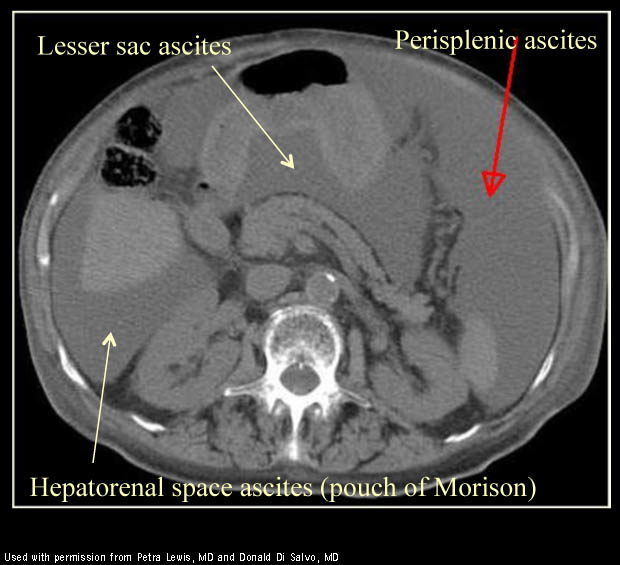
Small amounts of ascitic fluid localize in the right perihepatic space the posterior subhepatic space i e morison s pouch and the pouch of douglas.
B ct scan of the pelvis shows that the bowel loops of the oral aspect of the intestine are dilated arrowhead and the bowel loops of the anal aspect are collapsed arrow.
Ascites is well demonstrated by ct.